RAP - Classic Pattern
In this article, we look at the Classic Pattern and discuss the use cases of its implementation in ABAP Cloud.
Table of contents
In this article, we will look at the classic pattern for developing RAP objects in the system, discussing the various points of attention and distinctions.
Introduction
The ABAP RESTful Application Programming Model is the new model in ABAP for creating Cloud Ready and Clean Core applications. With RAP, you can not only create applications but also provide interfaces for internal and external use. With the latest features, RAP is very flexible in terms of structure and use, which is why we would like to divide the applications into different patterns.
Structure
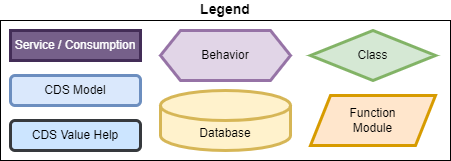
The "Classic Pattern" It is named this way because it embodies the foundation of RAP and thus provides all development possibilities locally. If you want to start learning RAP, you should start with this model. To begin with, here is the legend for the model.
The following characteristics serve to differentiate it:
- Main data is stored locally in its own tables
- Creation of a separate data model in the managed scenario
- Search helps from local data, but remote access is also possible
This behavior has been defined as optional for now, since you can also implement a pure display application. If you want to change the data or further influence the logic, you should also define a behavior and can implement additional logic there, such as validations, determinations or additional actions.
Model
In this chapter, we'll take a look at where the model is used and how you can use it in conjunction with search helps.
Usage
In addition to the manual development of the entire RAP stack, three different RAP generators are currently available. Once you've learned RAP, the generators will help you create models and applications quickly and easily, significantly reducing development time. The applications then need to be further developed manually.
Search Helps
If you implement a search help in the Classic Pattern, the data is usually located in the same system. This makes implementation quick and easy. In this scenario, however, it is also possible to connect a remote source via a custom entity and use it as a value help; this would not initially change the behavior or the type of implementation.
Learning
If you are approaching classic development with the ABAP RESTful Application Programming Model, you should start with a simple example. If you already have experience with BOPF and OData, getting started with development should be much easier, as you'll already have internalized the concepts. For more details on learning the new programming model, see the article on Programming Models.
More Examples
If you'd like to check out some resources related to the article, you'll find many examples from past articles in our GitHub repository. You can find examples in the following packages in the repository:
- ZBS_DEMO_RAP_SIMPLE - Simple example to test common RAP implementations and functions.
- ZBS_DEMO_RAP_COMPLEXE - Multi-level RAP object to test the hierarchy and multiple nodes.
- ZBS_DEMO_RAP_GOOGLE - Example of a RAP application for translating texts with a connection to the Google API.
Conclusion
The Classic Pattern is the standard case in development and should be learned first by you as a developer. This will give you all the basics of RAP development and how the different layers behave.