ABAP Cloud - Prepare date
How can you actually get a date in ABAP Cloud into the appropriate output format? Let's look at an example in the system.
Table of contents
In this article, we'll look at different ways you can prepare a date for output, what options are available, and how you can use them.
Introduction
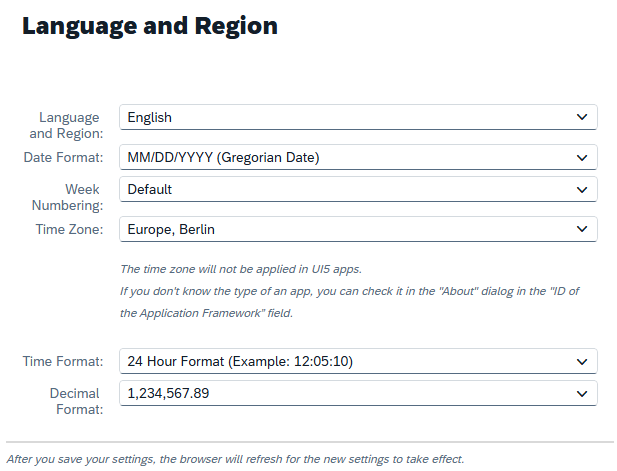
Normally, the system handles date preparation for you, for example, when a date is displayed in the Fiori UI. Depending on the language selected and the user's other settings, the date can be displayed and prepared accordingly. This is called an external format.
If we look at a date in ABAP format, i.e., at runtime in the system, the date always follows the same rule to be converted from there to the external format. We need this kind of formatting, for example, when printing or sending emails.
String Template
String templates have been around for quite some time, and they allow you to easily combine different texts and format them accordingly. For example, if we want to output a date in the currently set user format, we can select the USER format from the DATE area. You can find documentation for other formats linked below in the article.
output = |{ actual_date DATE = USER }|.
However, this formatting is of no use if we want a specific format. For example, if we want the current format for Germany, we can specify the COUNTRY suffix. In principle, this also works for other data types, such as times, numbers, or timestamps.
output = |{ actual_date COUNTRY = 'DE ' }|.
If you look at the output, the space in DE is intentional. Without the space, the compiler displays an error message and informs us of the correct format.
CL_ABAP_DATFM
An alternative to the string templates is the CL_ABAP_DATFM class, which is also released for ABAP Cloud. This offers numerous helper methods for preparing data at runtime. Let's take a look at the class's public methods.
We have some check methods that begin with CHECK, some GET methods to read various settings, and the CONV methods to perform specific conversions. In the first step, we need to determine the date format for the country. This is derived from the country customization. Then we call the conversion using the format. However, with the class, we also need to handle error handling and catch the exception.
DATA(format_de) = cl_abap_datfm=>get_country_datfm( 'DE' ).
TRY.
cl_abap_datfm=>conv_date_int_to_ext( EXPORTING im_datint = actual_date
im_datfmdes = format_de
IMPORTING ex_datext = output ).
CATCH cx_abap_datfm_format_unknown.
ENDTRY.
We can also use a similar method if, for example, we want the short date without the year. In this example, we generate the output for the USA.
DATA(format_us) = cl_abap_datfm=>get_country_datfm( 'US' ).
TRY.
cl_abap_datfm=>conv_date_int_to_shortex( EXPORTING im_datint = actual_date
im_datfmdes = format_us
IMPORTING ex_abbrdatext = output ).
CATCH cx_abap_datfm_format_unknown.
ENDTRY.
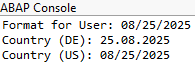
Finally, let's look at the result in the console, where we can compare the different methods. The added value of the class lies primarily in the numerous ways to display a date and also to obtain formats for a year or a short date.
Complete Example
Here you can find the complete example of the code snippets shown above in the complete class. You can copy the example into your system and start experimenting right away.
CLASS zcl_bs_demo_date_conversion DEFINITION
PUBLIC FINAL
CREATE PUBLIC.
PUBLIC SECTION.
INTERFACES if_oo_adt_classrun.
PRIVATE SECTION.
DATA out TYPE REF TO if_oo_adt_classrun_out.
DATA output TYPE string.
METHODS print
IMPORTING !description TYPE string DEFAULT ``.
METHODS use_string_template
IMPORTING actual_date TYPE d.
METHODS use_datfm_class
IMPORTING actual_date TYPE d.
ENDCLASS.
CLASS zcl_bs_demo_date_conversion IMPLEMENTATION.
METHOD if_oo_adt_classrun~main.
me->out = out.
DATA(actual_date) = zcl_syst=>create( )->system_date( ).
use_string_template( actual_date ).
use_datfm_class( actual_date ).
ENDMETHOD.
METHOD print.
IF description IS INITIAL.
out->write( output ).
ELSE.
out->write( |{ description }: { output }| ).
ENDIF.
ENDMETHOD.
METHOD use_string_template.
output = |{ actual_date DATE = USER }|.
print( `Format for User` ).
output = |{ actual_date COUNTRY = 'DE ' }|.
print( `Country (DE)` ).
output = |{ actual_date COUNTRY = 'US ' }|.
print( `Country (US)` ).
ENDMETHOD.
METHOD use_datfm_class.
DATA(format_de) = cl_abap_datfm=>get_country_datfm( 'DE' ).
DATA(format_us) = cl_abap_datfm=>get_country_datfm( 'US' ).
TRY.
cl_abap_datfm=>conv_date_int_to_ext( EXPORTING im_datint = actual_date
im_datfmdes = format_de
IMPORTING ex_datext = output ).
print( `DATFM Date (DE)` ).
CATCH cx_abap_datfm_format_unknown.
ENDTRY.
TRY.
cl_abap_datfm=>conv_date_int_to_shortex( EXPORTING im_datint = actual_date
im_datfmdes = format_us
IMPORTING ex_abbrdatext = output ).
print( `DATFM Shortex (US)` ).
CATCH cx_abap_datfm_format_unknown.
ENDTRY.
TRY.
cl_abap_datfm=>conv_date_int_to_shortex( EXPORTING im_datint = actual_date
im_datfmdes = format_de
IMPORTING ex_abbrdatext = output ).
print( `DATFM Shortex (DE)` ).
CATCH cx_abap_datfm_format_unknown.
ENDTRY.
ENDMETHOD.
ENDCLASS.
Conclusion
Preparing dates doesn't always have to be difficult. SAP provides several alternatives in ABAP Cloud that are quite easy to use to achieve the correct target format. This saves you from having to access substrings to get the date into the correct format, especially when it comes to country-specific formats.
Source:
SAP Help - String Template (Format options)
ABAP Cloud - System Fields