CDS - Data model
In this article we want to introduce you to the data model that we will be working with in the future. You should be able to use it as well.
Table of contents
Article update: Since release 7.57 (S/4 HANA 2022), DEFINE VIEW is marked as obsolete, you should use DEFINE VIEW ENTITY instead. These may differ from the examples in some places. You can find more information about the new views in this article.
We already used the first elements from the new data model in a previous article. In this article we want to introduce the data model, the tables and the associated interface views in more detail. At the end you should also have the opportunity to create the data model and generate test data.
Tables
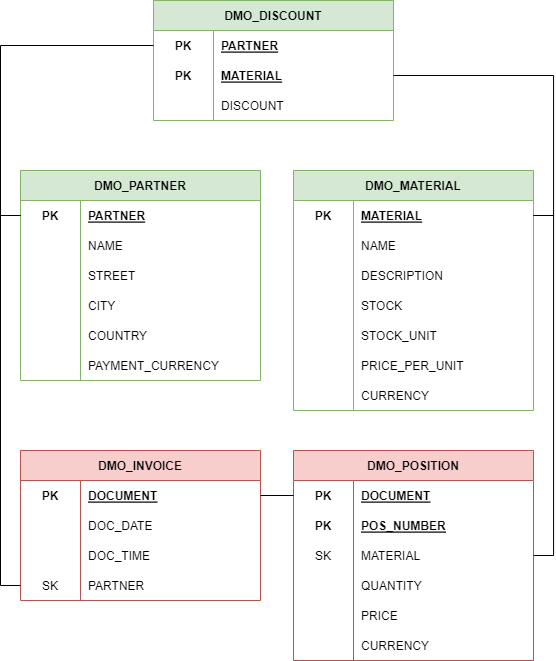
We set up a small model with three master data tables and two transaction data tables, the focus here is on the partner with whom we do business, the material table and the invoice that is sent. The data model therefore looks as follows.
In addition, the invoice has different items and a partner can get a discount on different materials. The tables are linked via the primary and secondary keys. To do this, we now create the corresponding tables via Eclipse.
Partner
@EndUserText.label : 'Partner Data'
@AbapCatalog.enhancement.category : #NOT_EXTENSIBLE
@AbapCatalog.tableCategory : #TRANSPARENT
@AbapCatalog.deliveryClass : #A
@AbapCatalog.dataMaintenance : #RESTRICTED
define table zbs_dmo_partner {
key client : abap.clnt not null;
key partner : abap.char(10) not null;
name : abap.char(60);
street : abap.char(80);
city : abap.char(60);
country : land1;
payment_currency : abap.cuky;
}
Material
@EndUserText.label : 'Material Data'
@AbapCatalog.enhancement.category : #NOT_EXTENSIBLE
@AbapCatalog.tableCategory : #TRANSPARENT
@AbapCatalog.deliveryClass : #A
@AbapCatalog.dataMaintenance : #RESTRICTED
define table zbs_dmo_material {
key client : abap.clnt not null;
key material : abap.char(5) not null;
name : abap.char(25);
description : abap.char(150);
@Semantics.quantity.unitOfMeasure : 'zbs_dmo_material.stock_unit'
stock : abap.quan(10,0);
stock_unit : abap.unit(3);
@Semantics.amount.currencyCode : 'zbs_dmo_material.currency'
price_per_unit : abap.curr(15,2);
currency : abap.cuky;
}
Discount
@EndUserText.label : 'Discount Data'
@AbapCatalog.enhancement.category : #NOT_EXTENSIBLE
@AbapCatalog.tableCategory : #TRANSPARENT
@AbapCatalog.deliveryClass : #A
@AbapCatalog.dataMaintenance : #RESTRICTED
define table zbs_dmo_discount {
key client : abap.clnt not null;
key partner : abap.char(10) not null;
key material : abap.char(5) not null;
discount : abap.dec(5,2);
}
Invoice
@EndUserText.label : 'Invoice Data'
@AbapCatalog.enhancement.category : #NOT_EXTENSIBLE
@AbapCatalog.tableCategory : #TRANSPARENT
@AbapCatalog.deliveryClass : #A
@AbapCatalog.dataMaintenance : #RESTRICTED
define table zbs_dmo_invoice {
key client : abap.clnt not null;
key document : abap.char(8) not null;
doc_date : abap.dats;
doc_time : abap.tims;
partner : abap.char(10);
}
Invoice position
@EndUserText.label : 'Invoice Position Data'
@AbapCatalog.enhancement.category : #NOT_EXTENSIBLE
@AbapCatalog.tableCategory : #TRANSPARENT
@AbapCatalog.deliveryClass : #A
@AbapCatalog.dataMaintenance : #RESTRICTED
define table zbs_dmo_position {
key client : abap.clnt not null;
key document : abap.char(8) not null;
key pos_number : abap.int2 not null;
material : abap.char(5);
@Semantics.quantity.unitOfMeasure : 'zbs_dmo_material.stock_unit'
quantity : abap.quan(10,0);
@Semantics.amount.currencyCode : 'zbs_dmo_position.currency'
price : abap.curr(15,2);
currency : abap.cuky;
}
Hint: As you have probably noticed, we also use annotations when creating tables to link currencies and quantity fields.
Core Data Services
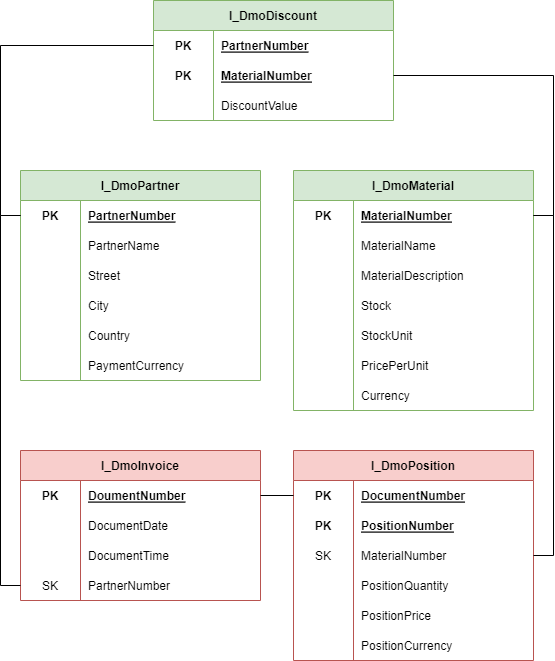
Every clean data model has a basis with Interface or Basic Views, on which the further layers of the model are built. We also have the option of standardizing the field names and making them unique in the entire data model. The data model looks like this:
The fields in the data model are now unique, making it easier to merge the data into new views. Each field name thus describes a unique task. The CDS views now look like this.
Partner
@AbapCatalog.sqlViewName: 'ZBSIDMOPARTNER'
@AbapCatalog.compiler.compareFilter: true
@AbapCatalog.preserveKey: true
@AccessControl.authorizationCheck: #NOT_REQUIRED
@EndUserText.label: 'Interface for Partner'
define view ZBS_I_DmoPartner
as select from zbs_dmo_partner
{
key partner as PartnerNumber,
name as PartnerName,
street as Street,
city as City,
country as Country,
payment_currency as PaymentCurrency
}
Material
@AbapCatalog.sqlViewName: 'ZBSIDMOMATERIAL'
@AbapCatalog.compiler.compareFilter: true
@AbapCatalog.preserveKey: true
@AccessControl.authorizationCheck: #NOT_REQUIRED
@EndUserText.label: 'Interface for Material'
define view ZBS_I_DmoMaterial
as select from zbs_dmo_material
{
key material as MaterialNumber,
name as MaterialName,
description as MaterialDescription,
stock as Stock,
stock_unit as StockUnit,
price_per_unit as PricePerUnit,
currency as Currency
}
Discount
@AbapCatalog.sqlViewName: 'ZBSIDMODISCOUNT'
@AbapCatalog.compiler.compareFilter: true
@AbapCatalog.preserveKey: true
@AccessControl.authorizationCheck: #NOT_REQUIRED
@EndUserText.label: 'Interface for Discount'
define view ZBS_I_DmoDiscount
as select from zbs_dmo_discount
{
key partner as PartnerNumber,
key material as MaterialNumber,
discount as DiscountValue
}
Invoice
@AbapCatalog.sqlViewName: 'ZBSIDMOINVOICE'
@AbapCatalog.compiler.compareFilter: true
@AbapCatalog.preserveKey: true
@AccessControl.authorizationCheck: #NOT_REQUIRED
@EndUserText.label: 'Interface for Invoice'
define view ZBS_I_DmoInvoice
as select from zbs_dmo_invoice
{
key document as DocumentNumber,
doc_date as DocumentDate,
doc_time as DocumentTime,
partner as PartnerNumber
}
Invoice position
@AbapCatalog.sqlViewName: 'ZBSIDMOPOSITION'
@AbapCatalog.compiler.compareFilter: true
@AbapCatalog.preserveKey: true
@AccessControl.authorizationCheck: #NOT_REQUIRED
@EndUserText.label: 'Interface for Position'
define view ZBS_I_DmoPosition
as select from zbs_dmo_position
{
key document as DocumentNumber,
key pos_number as PositionNumber,
material as MaterialNumber,
quantity as PositionQuantity,
price as PositionPrice,
currency as PositionCurrency
}
Test data
Nothing beats good test data, or just a certain amount of test data to work with as a developer. For this we write a small class with which the data can be easily generated. For the receipts and items, you can also configure the number and variance of the items. You can find all the sample code here:
CLASS zcl_bs_demo_dummy_data DEFINITION PUBLIC FINAL CREATE PUBLIC.
PUBLIC SECTION.
INTERFACES if_oo_adt_classrun.
CONSTANTS:
c_error TYPE zbs_dmo_position-price VALUE '37707',
c_number_of_invoices TYPE i VALUE 300,
c_days_back_from_today TYPE i VALUE 365,
c_max_number_of_positions TYPE i VALUE 3,
c_max_quantity_per_position TYPE i VALUE 5.
PROTECTED SECTION.
PRIVATE SECTION.
DATA:
mt_partner TYPE STANDARD TABLE OF zbs_dmo_partner,
mt_material TYPE STANDARD TABLE OF zbs_dmo_material,
mt_discount TYPE STANDARD TABLE OF zbs_dmo_discount,
mt_head TYPE STANDARD TABLE OF zbs_dmo_invoice,
mt_position TYPE STANDARD TABLE OF zbs_dmo_position,
mo_random_partner TYPE REF TO zcl_bs_demo_random,
mo_random_date TYPE REF TO zcl_bs_demo_random,
mo_random_position TYPE REF TO zcl_bs_demo_random,
mo_random_material TYPE REF TO zcl_bs_demo_random,
mo_random_quantity TYPE REF TO zcl_bs_demo_random.
METHODS:
create_partner,
create_material,
create_discount,
create_invoice
IMPORTING
id_count TYPE i,
create_head
RETURNING
VALUE(rs_result) TYPE zbs_dmo_invoice,
create_positions
IMPORTING
is_head TYPE zbs_dmo_invoice.
ENDCLASS.
CLASS zcl_bs_demo_dummy_data IMPLEMENTATION.
METHOD if_oo_adt_classrun~main.
create_partner( ).
out->write( |Partner: { lines( mt_partner ) }| ).
create_material( ).
out->write( |Material: { lines( mt_material ) }| ).
create_discount( ).
out->write( |Discount: { lines( mt_discount ) }| ).
create_invoice( c_number_of_invoices ).
out->write( |Invoice: { lines( mt_head ) }| ).
out->write( |Position: { lines( mt_position ) }| ).
ENDMETHOD.
METHOD create_partner.
mt_partner = VALUE #(
( partner = '1000000000' name = 'SAP' street = 'Demo Street 15' city = 'Walldorf' country = 'DE' payment_currency = 'EUR' )
( partner = '1000000001' name = 'Microsoft' street = 'Demo Street 24' city = 'Redmond' country = 'US' payment_currency = 'USD' )
( partner = '1000000002' name = 'Meta' street = 'Fox Street 1' city = 'Menlo Park' country = 'US' payment_currency = 'USD' )
( partner = '1000000003' name = 'Alibaba' street = 'Alley 15' city = 'Hangzhou' country = 'CN' payment_currency = 'CNY' )
( partner = '1000000004' name = 'BMW' street = 'Main Avenue 200' city = 'Munich' country = 'DE' payment_currency = 'EUR' )
( partner = '1000000005' name = 'Nestle' street = 'Village Alley 14' city = 'Vevey' country = 'CH' payment_currency = 'CHF' )
( partner = '1000000006' name = 'Gazprom' street = 'Peace Avenue 1' city = 'Sankt Petersburg' country = 'RU' payment_currency = 'RUB' )
).
DELETE FROM zbs_dmo_partner.
INSERT zbs_dmo_partner FROM TABLE @mt_partner.
ENDMETHOD.
METHOD create_material.
mt_material = VALUE #(
( material = 'F0001'
name = 'Peanuts'
description = 'Roasted Peanuts from US'
stock = '900'
stock_unit = 'ST'
price_per_unit = '2.50'
currency = 'USD' )
( material = 'F0002'
name = 'Rice'
description = 'Big bag rice from china'
stock = '120'
stock_unit = 'BAG'
price_per_unit = '12.00'
currency = 'USD' )
( material = 'F0003'
name = 'Eggs'
description = 'Eggs from happy german chickens'
stock = '550'
stock_unit = 'PAK'
price_per_unit = '3.15'
currency = 'EUR' )
( material = 'H0001'
name = 'USB Stick 128 GB'
description = 'USB Stick with security features'
stock = '30'
stock_unit = 'ST'
price_per_unit = '49.99'
currency = 'EUR' )
( material = 'H0002'
name = 'OLED Display 34"'
description = 'Big and wide display with HDMI and dsiplay port'
stock = '18'
stock_unit = 'ST'
price_per_unit = '440.00'
currency = 'USD' )
( material = 'R0001'
name = 'Gas'
description = 'Gas from sibiria'
stock = '50000'
stock_unit = 'MMQ'
price_per_unit = '1560.00'
currency = 'RUB' )
).
DELETE FROM zbs_dmo_material.
INSERT zbs_dmo_material FROM TABLE @mt_material.
ENDMETHOD.
METHOD create_discount.
mt_discount = VALUE #(
( partner = '1000000000' material = 'F0003' discount = '10.00' )
( partner = '1000000001' material = 'F0001' discount = '15.00' )
( partner = '1000000001' material = 'H0002' discount = '3.50' )
( partner = '1000000006' material = 'R0001' discount = '7.50' )
).
DELETE FROM zbs_dmo_discount.
INSERT zbs_dmo_discount FROM TABLE @mt_discount.
ENDMETHOD.
METHOD create_invoice.
DO id_count TIMES.
DATA(ls_head) = create_head( ).
create_positions( ls_head ).
ENDDO.
DELETE FROM zbs_dmo_invoice.
INSERT zbs_dmo_invoice FROM TABLE @mt_head.
DELETE FROM zbs_dmo_position.
INSERT zbs_dmo_position FROM TABLE @mt_position.
ENDMETHOD.
METHOD create_head.
DATA:
ld_document TYPE n LENGTH 8 VALUE 30000000.
IF mo_random_partner IS INITIAL.
mo_random_partner = NEW #( id_min = 1 id_max = lines( mt_partner ) ).
mo_random_date = NEW #( id_min = 1 id_max = c_days_back_from_today ).
ENDIF.
rs_result = VALUE #(
document = ld_document + lines( mt_head )
doc_date = CONV d( cl_abap_context_info=>get_system_date( ) - mo_random_date->rand( ) )
doc_time = cl_abap_context_info=>get_system_time( )
partner = mt_partner[ mo_random_partner->rand( ) ]-partner
).
INSERT rs_result INTO TABLE mt_head.
ENDMETHOD.
METHOD create_positions.
IF mo_random_position IS INITIAL.
mo_random_position = NEW #( id_min = 1 id_max = c_max_number_of_positions ).
mo_random_material = NEW #( id_min = 1 id_max = lines( mt_material ) ).
mo_random_quantity = NEW #( id_min = 1 id_max = c_max_quantity_per_position ).
ENDIF.
DO mo_random_position->rand( ) TIMES.
DATA(ld_index) = sy-index.
DATA(ls_material) = mt_material[ mo_random_material->rand( ) ].
DATA(ld_quantity) = mo_random_quantity->rand( ).
TRY.
DATA(ld_discount) = mt_discount[ partner = is_head-partner material = ls_material-material ]-discount.
CATCH cx_sy_itab_line_not_found.
ld_discount = 0.
ENDTRY.
DATA(ls_position) = VALUE zbs_dmo_position(
document = is_head-document
pos_number = ld_index
material = ls_material-material
quantity = ld_quantity
price = ( ld_quantity * ls_material-price_per_unit ) * ( 1 - ld_discount / 100 )
currency = mt_partner[ partner = is_head-partner ]-payment_currency
).
TRY.
SELECT SINGLE FROM zbs_dmo_discount
FIELDS
currency_conversion(
amount = @ls_position-price,
source_currency = @ls_material-currency,
target_currency = @ls_position-currency,
exchange_rate_date = @is_head-doc_date,
round = @abap_true
) AS price
INTO @ls_position-price.
CATCH cx_sy_open_sql_db.
ls_position-price = c_error.
ENDTRY.
INSERT ls_position INTO TABLE mt_position.
ENDDO.
ENDMETHOD.
ENDCLASS.
When creating it, we rely on a mixture of fixed master data and random positions, using the random number generator from another article. This randomly derives the number of items, partners, and units sold, giving us a far-reaching result set. The coding has no special features, except for one case:
TRY.
SELECT SINGLE FROM zbs_dmo_discount
FIELDS
currency_conversion(
amount = @ls_position-price,
source_currency = @ls_material-currency,
target_currency = @ls_position-currency,
exchange_rate_date = @is_head-doc_date,
round = @abap_true
) AS price
INTO @ls_position-price.
CATCH cx_sy_open_sql_db.
ls_position-price = c_error.
ENDTRY.
Here we use a "dummy" select to do the currency conversion without a function module and use the standard ABAP-SQL function for it. In the event of an error that the conversion does not work, an error code is transferred to the field.
GitHub
All resources related to the Core Data Service series will be made available on GitHub this time for your convenience. You can use the link to find our repository and load the model into your system. The classes and the model are also Cloud Ready for use in the BTP. However, the class for the random number generator is not included in this package.
Conclusion
For a decent test you need a corresponding data model and also test data. In this article, we wanted to bring you closer to the model and provide you with the opportunity to use it.